
Yes, a tax attorney can negotiate with the IRS on your behalf,reducing penalties and resolving tax debt.Call our IRS tax relief attorney at (888) 342-9436.





Benjamin Franklin famously stated that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, a concept that is particularly applicable to the complexities of penalty abatement. Whether opting for legal representation or managing the process independently, it’s essential to grasp the key factors that impact penalty abatement decisions. This article examines the criteria for reasonable cause, first-time penalty abatement, and administrative waivers. We’ll assess the advantages and disadvantages of hiring legal help, detail the procedures for applying on your own, and offer a cost comparison to assist you in making a well-informed choice. For optimal outcomes in dealing with IRS tax penalty relief, penalty waiver requests, or first-time abatement, understanding terms like tax penalty, natural disaster, and penalty for failure to file vs failure to pay is essential.
Penalty abatement is a relief opportunity provided by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that allows taxpayers to have their penalties for failing to file or pay taxes forgiven under certain circumstances. In essence, penalty abatement is the IRS’s admission that everyone makes mistakes, including taxpayers who generally comply with tax laws but may have stumbled due to unforeseen events or situations beyond their control.
Penalty abatement refers to the cancellation or reduction of penalties imposed by the IRS for noncompliance with tax filing and payment obligations. When taxpayers fail to meet these obligations, they may incur a variety of penalties. However, the IRS understands that not all transgressions are created equal. To ensure fairness, the agency assesses requests for penalty abatement by evaluating the taxpayer’s explanation against reasonable cause criteria detailed in the Internal Revenue Manual.
As part of the process, individuals must demonstrate a genuine reason for their failure to comply, such as income disruption, overwhelming medical expenditures, or other significant obstacles. The IRS also offers what is known as “First Time Penalty Abatement” for those with a clean penalty history, commending their general adherence to tax laws in the past. Taxpayers can formally make this request by filing IRS Form 843 and including relevant details such as the tax period in question, the amount and type of penalty, and their argument for reasonable cause.
Penalty abatement plays a significant role in tax management, acting as a key option for taxpayers to lessen the financial burden imposed by penalties. This relief is important as it helps reduce both the penalties and the interest accumulated on unpaid taxes, effectively lowering the overall debt owed to the IRS.
For those encountering penalties for the first time, this policy is vital. It helps maintain financial stability and corrects tax statuses without the burden of additional penalties. This is particularly beneficial for those facing genuine hardships, acknowledging that even well-intentioned taxpayers can experience financial setbacks.
Addressing and correcting inadvertent tax errors through penalty abatement not only eases immediate financial strain but also restores confidence in handling tax duties. This process is crucial for taxpayers to feel reassured that the system allows for human error and unexpected challenges.
The IRS takes into account various factors that might affect a taxpayer’s ability to pay on time, such as lost income, high medical expenses, natural disasters, or having received incorrect advice. This consideration is a testament to the IRS’s dedication to equitable tax administration.
To enhance the chances of successful penalty abatement, engaging with tax advisors or attorneys is advisable. These professionals provide the necessary expertise to present a convincing case to the IRS, helping transform a challenging tax issue into a solvable problem.
If you want to present a convincing case to the IRS, contact our team of experienced professionals today. We can help transform a challenging tax issue into a solvable problem.
It’s essential for taxpayers to file all required tax returns and settle any due taxes, or at least arrange a payment plan, before requesting penalty abatement. Compliance demonstrates a proactive approach to managing tax responsibilities.
Aspect | Advantages of Self-Application | Disadvantages of Self-Application |
Initial Contact | Taxpayers can initiate penalty relief by verbally contacting the nearest IRS office, which can quickly start the abatement process without the need for immediate written formalities. | Tax penalties can significantly increase the amount owed, often unexpectedly, as penalties are applied. This sudden increase can be shocking and overwhelming. |
Document Submission | It is advisable to submit copies instead of original documents when supporting an abatement request, thus ensuring the safeguarding of personal records. | The IRS applies penalties routinely without assessing individual circumstances, making the process stringent and often perceived as inflexible. |
Reapplication | If an initial plea is denied, discovering new information related to the tax issue allows for a new attempt at abatement, making it possible to adjust the strategy based on fresh evidence. | If a taxpayer’s reasonable cause is not accepted, the burden of proof is high. The taxpayer must demonstrate normal business care despite the circumstances that led to the delay. Failure to establish reasonable cause leaves the penalties in force, compounding financial strain. |
Due Diligence | Demonstrating due diligence by waiting to gather all necessary data before submitting an accurate tax return can strengthen a case for abatement, especially if it establishes the presence of circumstances beyond the taxpayer’s control. | Managing one’s own penalty abatement process can be stressful, especially when dealing with the IRS directly. The process can exacerbate feelings of frustration and helplessness, especially when penalties and accrued interest significantly compound existing tax debts. |
Credibility | Establishing circumstances beyond one’s control lends credibility to requests for reasonable cause, potentially leading to successful penalty relief. | A lack of professional guidance can hinder the effectiveness of presenting a case for reasonable cause, potentially leading to the retention of penalties. |
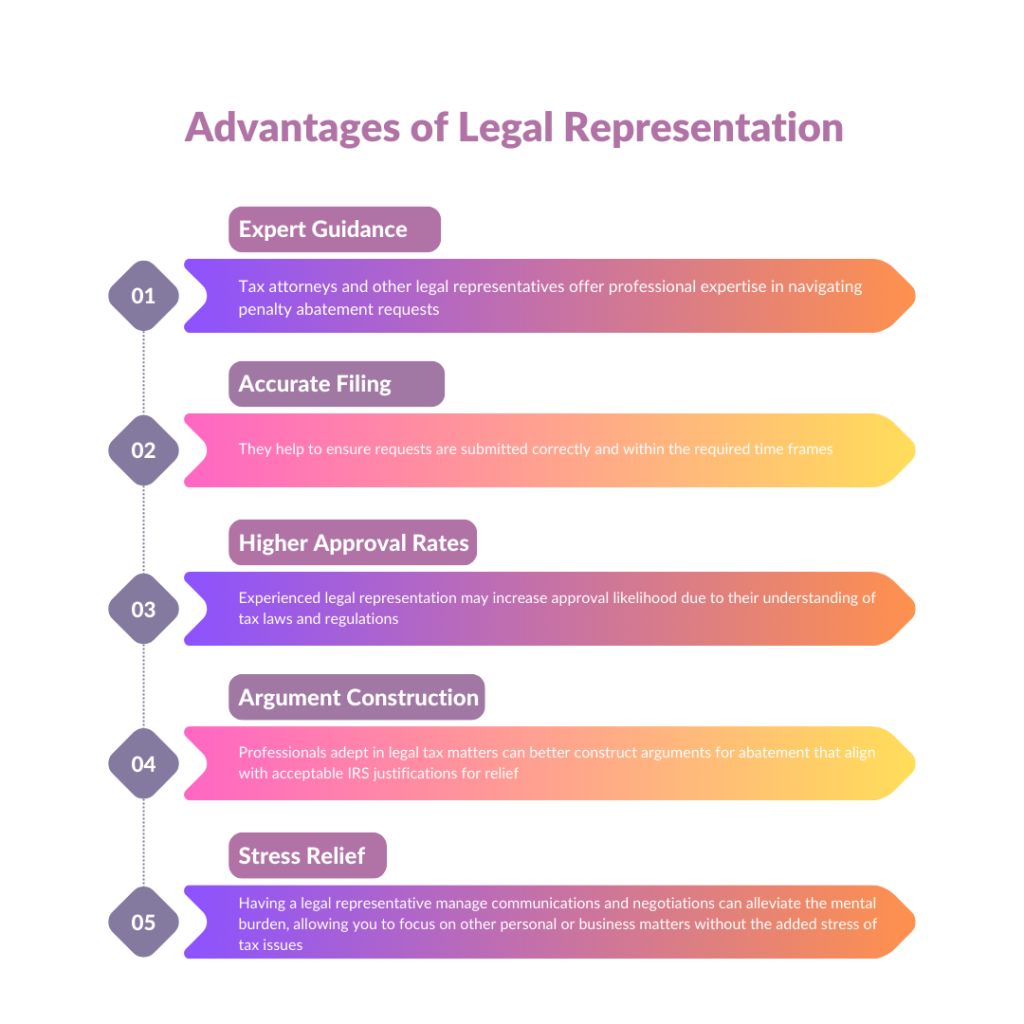
Dealing with the IRS and its rules can be tough, especially with penalty abatement issues. Getting help from experienced tax professionals like tax attorneys or certified public accountants is key. These experts know tax law well and understand IRS protocols, which is crucial in making a strong case for penalty abatement. Their advice is very helpful for taxpayers facing penalties from unintended mistakes, often due to financial problems or wrong advice.
A clear and well-documented argument is essential for a strong appeal to tax authorities. The success of a penalty abatement request often hinges on the quality and relevance of the evidence provided. Therefore, obtaining expert legal representation can potentially turn a challenging situation into a manageable one.
The support of a tax professional can significantly boost the chances of an advantageous resolution. These individuals have a deep understanding of the IRS’s framework for penalty abatement, including the criteria for penalty waivers based on reasonable cause or specific IRS guidelines. They are skilled in filing the necessary documents, such as Form 843 (Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement), and understand the finer points of the process that could escape less experienced taxpayers.
Hiring legal help for penalty abatement has benefits, but there are also drawbacks. The main concern is the cost. Professional services are expensive. This might not be worthwhile, especially for small penalties. Adding a lawyer or tax advisor can also slow down the process. This happens because there are more steps in communicating with the IRS.
At J David Tax Law, we recognize these concerns and are committed to providing cost-effective legal solutions to make professional representation accessible to everyone. Contact us today at (888) 342-9436 to discuss how we can provide effective yet affordable legal support for your IRS penalty issues.
A brief rundown of the disadvantages includes:
Legal representation typically involves service fees that may be substantial.
Introducing a third party can extend processing times for abatement requests.
Direct interaction between taxpayers and the IRS may be limited when using legal representation.
The addition of a legal layer may introduce complex procedural requirements that can be time-consuming to understand and address.
The strategies preferred by legal representatives may not always match the taxpayer’s personal approach, potentially affecting the outcome.
Our tax relief attorneys specialize in tax problems and tax debt resolutions
Get started with a 100% free consultation

Yes, a tax attorney can negotiate with the IRS on your behalf,reducing penalties and resolving tax debt.Call our IRS tax relief attorney at (888) 342-9436.

Missed the April 15 Tax Day 2025 deadline? Learn about IRS penalties, late payment relief, and how to settle your tax debt. Call us at (888) 342-9436.

IRS grants a tax deadline extension to California wildfire victims.Can you delay filing and payment until Oct. 15, 2025?Call at (888) 342-9436 to find out.
Get IRS Tax Assistance Within 24 Hours